Overview
The Chugoku-Shikoku Region is a collective term combining the Chugoku and Shikoku Regions. The former is the western portion of Honshu, the main island of Japan, and it consists of five prefectures: Yamaguchi, Hiroshima, Okayama, Tottori, and Shimane.
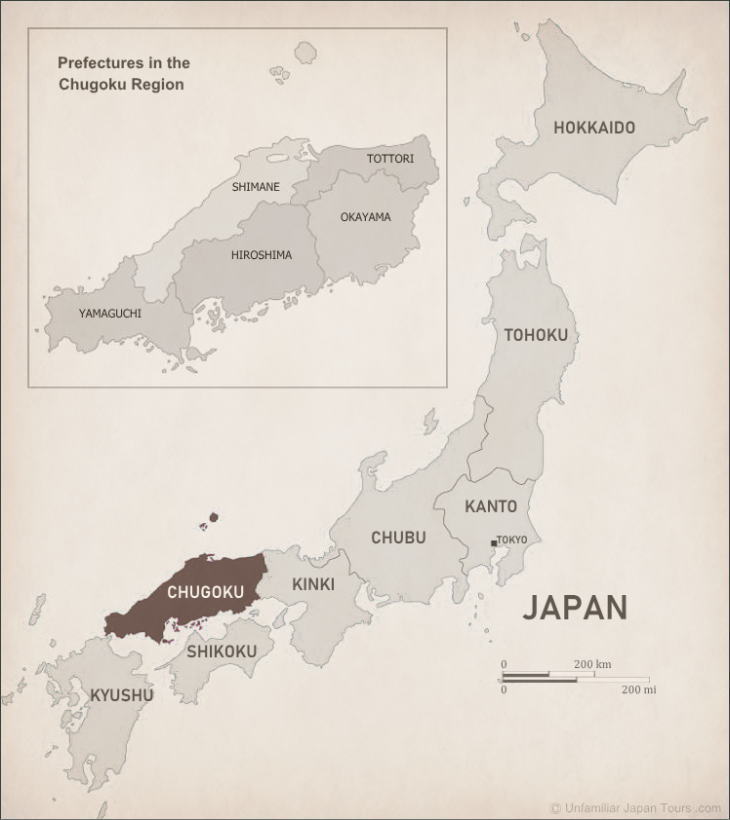
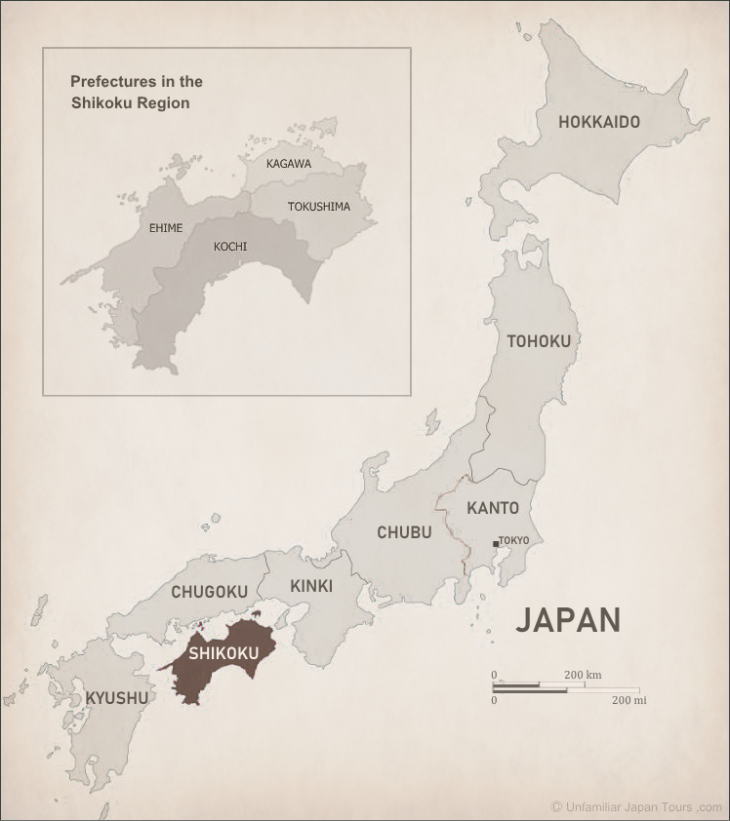
The latter is the smallest of the four large islands of Japan and consists of four prefectures: Ehime, Kagawa, Kochi, and Tokushima. The waters sandwiched between these two pieces of land are called the Seto Inland Sea.
The Chugoku Mountains stretch from east to west throughout the most of the Chugoku area. These are generally low and gently sloping mountains, with heights of 1,000 meters to 1,300 meters. There are many plateaus on the hillsides, and people often utilize them as a pasture for dairy/beef cattle.
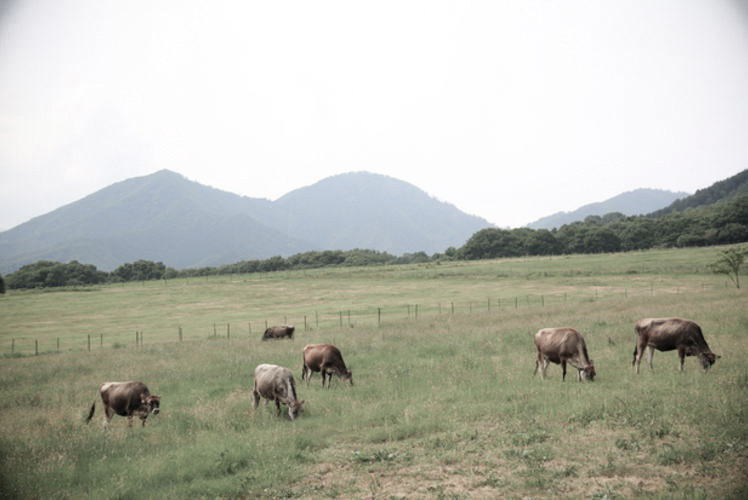

On the other hand, the Shikoku Mountains, which occupy a large portion of the Shikoku Island, are a succession of steep peaks and deep ravines. Many of the peaks reach nearly 2,000 meters and the highest one is Mt. Ishizuchi in Ehime Prefecture, which has a height of 1,982 meters.
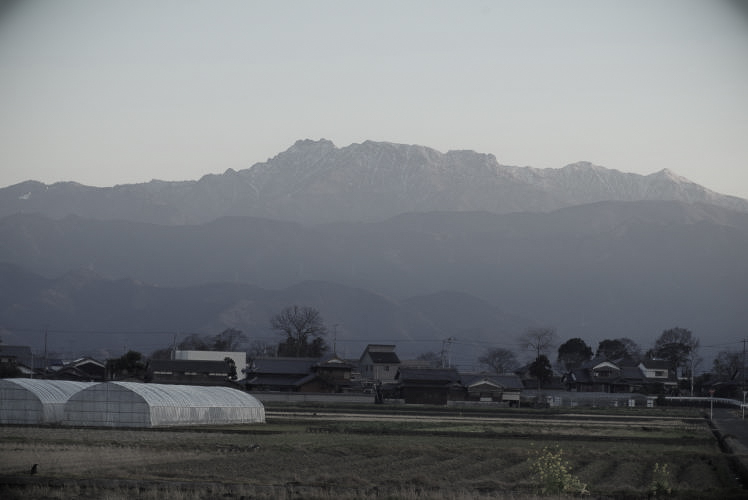

These two big mountain ranges often extend as close as the seashore, and this is why, in the Chugoku-Shikoku Region, the total percentage of flat lands is small, compared to the other six Regions.
Map of Chugoku and Shikoku
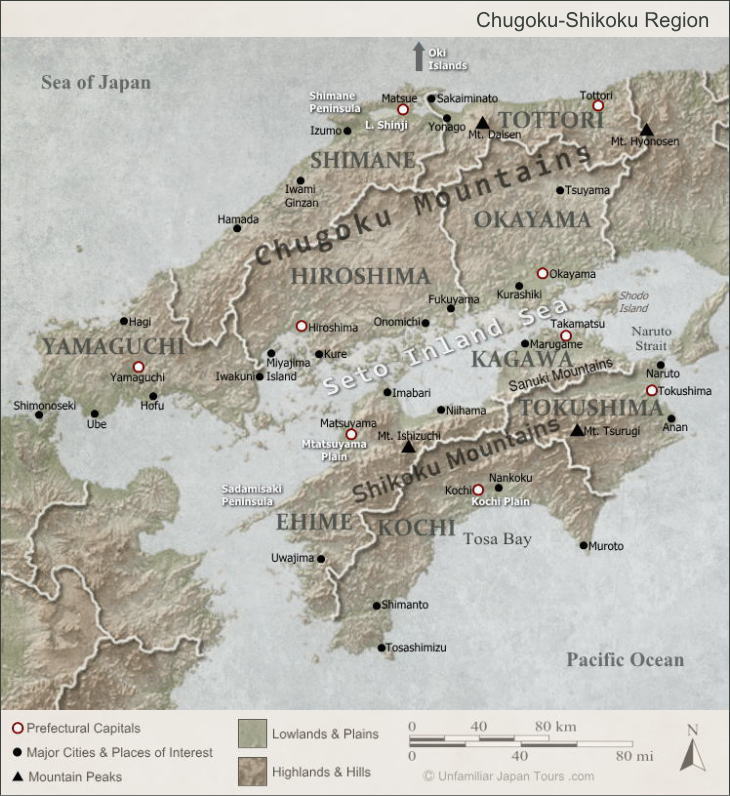
The Chugoku-Shikoku Region is often divided into three areas: San’in (pronounced as sun-inn), Setouchi, and Southern Shikoku. Each area has different characteristics, and in particular, the difference in climate is distinctive.
San’in Area
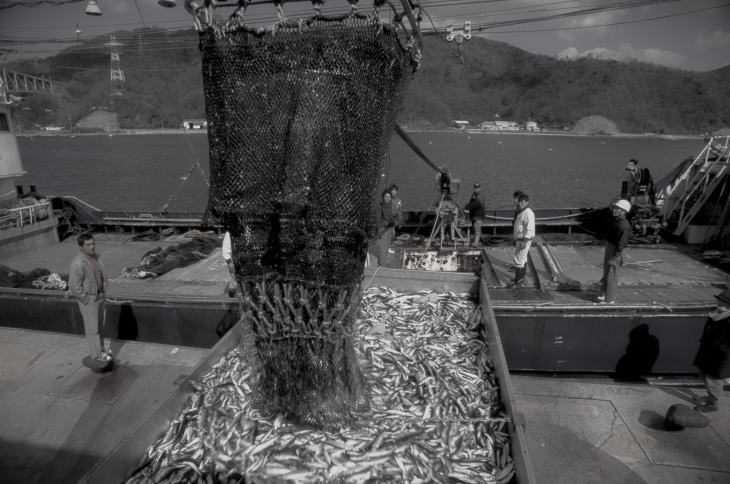
The San’in area is the area to the north side of the Chugoku Mountains. Bordering the Sea of Japan, a lot of snow falls here in winter, and there are many ski resorts in this mountainous area. But the coldness in the winter time is not so harsh because of the influence of the warm Tsushima Current that passes nearby. San’in is blessed with fertile fishing waters. In particular, the port of Sakai in Tottori Prefecture boasts of the large number of fish hauled in there.

San’in has many fascinating places to visit. Izumo Taisha Shrine in Shimane Prefecture is one of the oldest and most important Shinto shrines in Japan, with its founding stories often told in Japanese mythology. Mount Daisen is the highest mountain in the Chugoku Region at 1,729m, being one of the symbols of Tottori Prefecture. The surrounding areas of the mountain are designated as Daisen-Oki National Park, and the largest buna forest in Western Japan covers its slopes (Buna is a Japanese Siebold’s beech). Also, San’in has a number of towns and streets that preserve the historic atmosphere. And some of them are now tourism resources.

Setouchi Area
The Setouchi area consists of the Seto Inland Sea (Seto Naikai) and its surrounding land areas (which are the southern part of Chugoku and the northern part of Shikoku). This area boasts of the dry and sunny weather with a small amount of precipitation throughout the year. This is because the huge mountain ranges to the north and south shield the humid seasonal winds in summer and winter before they reach Setouchi. However, as a trade-off, people in Setouchi have struggled with repeated water shortages. To solve this problem, people have created a lot of reservoirs and irrigation canals.
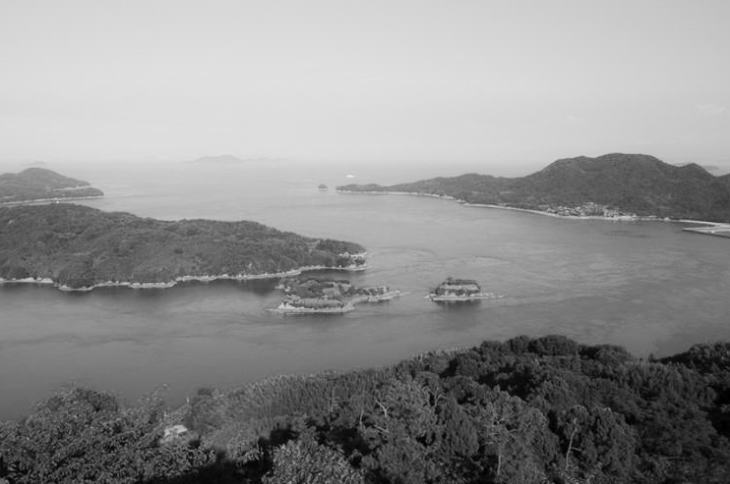

The Seto Inland Sea contains about 3,000 small islands. And it has been famous for its scenic beauty for centuries. In 1934, the sea and its surrounding areas became one of the first national parks in the country when they were designated as the Setonaikai National Park.
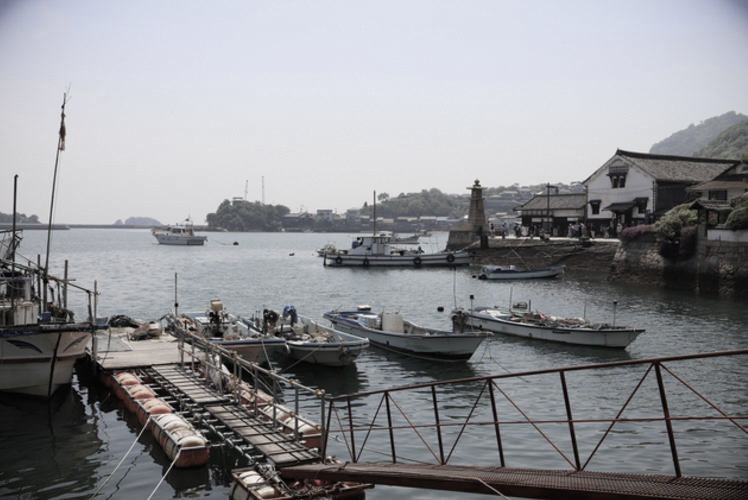

An Important Sea Route
In the Edo Period (1603 -1867), this sea played an important role as a sea route. The rice and marine products harvested in the north countries of Tohoku and Hokkaido were shipped to Osaka and Kyoto via the Seto Inland Sea. Small towns like Tomonoura in present-day Hiroshima Prefecture and Shimotsui in present-day Okayama Prefecture developed as the port towns for these ships. And when we visit these towns today and see their old, narrow streets, we can still get a sense of their past glories.
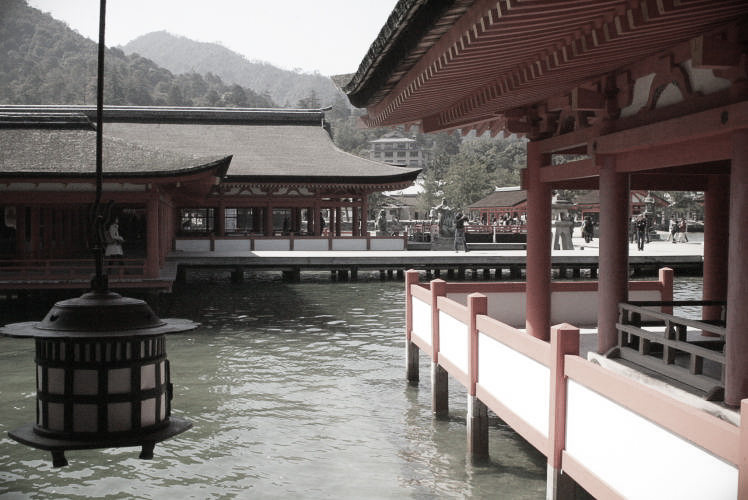

Among the numerous small islands dotting the Seto Inland Sea, the island of Itsukushima (also known as Miyajima) is especially famous. Since the mid-17th century, the island has been popular as one of the three most scenic places in the country and has been attracting many tourists and religious worshipers. And since 1996, when Itsukushima Shrine, the island’s main attraction, became a UNESCO World Heritage site, the number of visitors, including quite a few international travelers, has increased even more.
Southern Shikoku
Southern Shikoku is the area to the south side of the Shikoku Mountains. Under the influence of the Japan Current (Kuroshio) passing nearby, this area is characterized by its warm and rainy climate. The annual precipitation sometimes exceeds 4,000mm in the mountains (the nation’s annual average is 1,700mm), and typhoons often hit the area in autumn. Since the rain precipitates the growth of trees, such as cedar and Japanese cypress (hinoki), forestry has been one of the crucial ways to support the local people’s lives here (although the number of people engaging in forestry is decreasing). Other occupations prospering in South Shikoku include fishery in the Pacific Ocean and vegetable farming, including the wide spread use of greenhouses. In particular, Kochi Prefecture is Japan’s No.1 producer of several vegetables, including eggplant, ginger, myoga ginger, shishito pepper and yuzu (as of 2020).

Rivers in Southern Shikoku
Several rivers originate in the Shikoku Mountains, and after meandering through the land of South Shikoku, they eventually flow into the Pacific. Among those rivers, perhaps the Shimanto is the most famous. The river flows through the western part of Southern Shikoku without any large-scale dams. And people has called it ‘the last clear river in Japan’. The Niyodo River, which runs in the central part, is also known for its clear water. According to a survey conducted by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism in 2010, the water quality of this river is among the best in the country. Now these rivers have become weekend recreation spots for local residents and tourists alike.
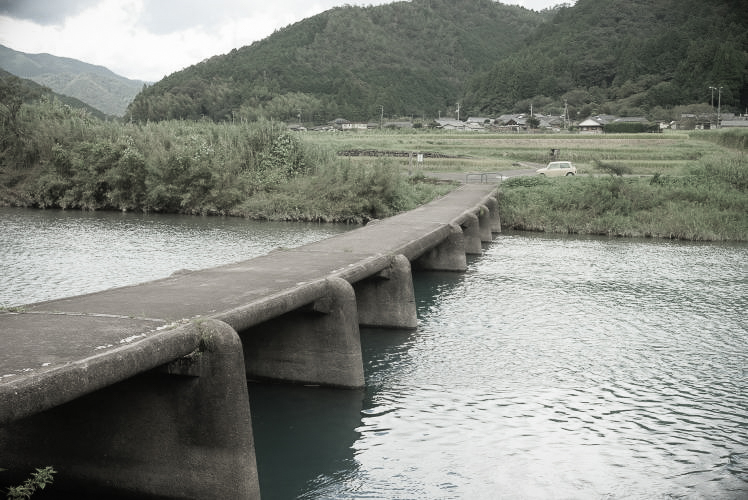

Chinka-bashi Bridges
On visiting these rivers, we can sometimes see an unusual type of bridge with no railings, which is constructed in the relatively lower position than normal bridges, with not so much distance between it and the surface of the river. This kind of bridge is called a low-water crossing or low-water bridge in English. In Japan, people commonly call it chinka-bashi (literally, “a sinking bridge”). If a river was flooded by a heavy rain, a normal bridge could be broken by floating objects like driftwood hitting its railings. So, people created those bridges with no railings, assuming that the bridges would be under the surface of the water when the river was swollen. Kochi Prefecture has the largest number of chinka-bashi in Japan, and the Shimanto River alone has nearly 50 of them. Of course, through these bridges, we can get a sense of the local people’s long-time struggle against the elements, but now some of these bridges have become popular tourist destinations.
Photographs: Properties of Unfamiliar Japan Tours.com, unless otherwise noted.
Outbound Links (New Window)


























